Lithium, the indispensable element powering our modern world, is once again demanding our focused attention. Its critical role in lithium-ion batteries, the workhorses behind everything from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles (EVs) and vast grid-scale energy storage arrays, places it at the nexus of technological advancement and global energy policy. The market has experienced a volatile period, with prices oscillating dramatically, and current upward trends suggest a potential shift with profound implications for both mining operations and the future of battery technology.
To fully appreciate the current landscape, a brief retrospective is in order. The year 2020 marked a significant inflection point, as global EV sales began their meteoric rise, consequently fueling an unprecedented surge in demand for lithium. This burgeoning demand, coupled with a constrained supply, sent prices soaring. Lithium carbonate, a key compound in battery production, witnessed a remarkable ascent, climbing from under $10 per kilogram to an astonishing high of approximately $70 per kilogram within a mere two-year span.
This dramatic price escalation did not go unnoticed by the technology sector. During these price peaks, there was a palpable surge in research and development efforts aimed at discovering and commercializing alternative battery chemistries that could lessen the reliance on lithium. This period saw intense exploration into technologies such as sodium-based batteries, which leverage the Earth’s abundant sodium resources, offering a potentially more cost-effective and sustainable alternative. Similarly, iron-air batteries emerged as a promising contender, utilizing iron and oxygen to generate electricity, with the potential for high energy density and lower material costs. Even more experimental avenues were explored, including the development of batteries constructed from plastic, pushing the boundaries of material science in the quest for cheaper and more accessible energy storage solutions.
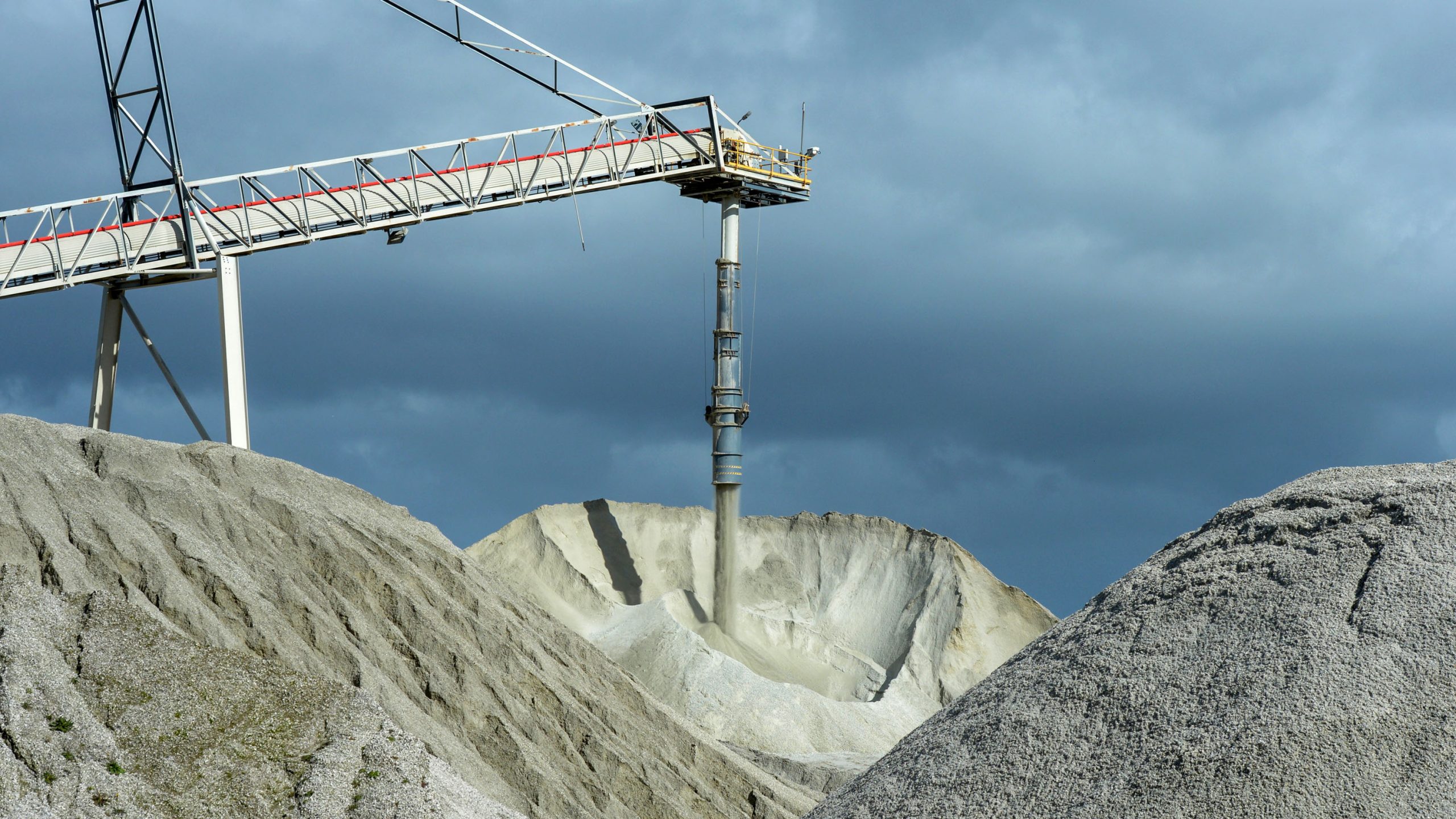
Simultaneously, the mining and materials science communities were actively seeking innovative ways to secure lithium supplies. Battery recycling emerged as a crucial area of focus, aiming to recover valuable lithium from end-of-life batteries, thereby reducing the need for virgin extraction. Furthermore, novel processing methods, such as direct lithium extraction (DLE), began to gain traction. DLE technologies offered the promise of extracting lithium more efficiently and with a reduced environmental footprint, particularly from brines and geothermal waters, which are often more accessible than hard-rock deposits.
However, the lithium market soon experienced a significant correction. A confluence of factors, including lower-than-anticipated EV demand in key markets like the US and a substantial ramp-up in mining and processing capacity, led to a dramatic price crash. By late 2024 and extending into 2025, lithium carbonate prices had fallen back to around $10 per kilogram. This price deflation diminished the urgency for lithium avoidance or the rapid development of alternative supply chains, leading to a temporary lull in the intense innovation seen during the preceding boom.
This brings us to the present moment, where lithium prices are once again on an upward trajectory. While the current price increases are not as dramatic as those experienced a few years ago, analysts are observing the trend with keen interest. A primary driver of this renewed demand is the robust growth of the EV market in China, which continues to represent approximately 75% of global battery demand. However, the expansion of stationary energy storage solutions, crucial for grid stability and the integration of renewable energy sources, is also contributing significantly to rising lithium demand, not only in China but also in the United States.
The prospect of higher lithium prices is, in turn, creating fertile ground for new opportunities and innovations. Evelina Stoikou, head of battery technologies and supply chains at BloombergNEF, highlights the potential for alternative battery chemistries to gain further traction. Notably, sodium-ion batteries have been recognized for their breakthrough potential, with MIT Technology Review including them on its list of 10 Breakthrough Technologies for 2026. This renewed focus on sodium-ion batteries is a direct response to the ongoing volatility and cost considerations associated with lithium, offering a promising pathway towards more affordable and sustainable energy storage.
Beyond the realm of batteries, the lithium price swing is poised to catalyze significant changes within the extraction and processing industries. Traditionally, the majority of lithium has been mined from hard-rock deposits, primarily in Australia, before being transported to China for processing. However, a growing global imperative to establish localized and secure lithium supply chains is driving efforts to diversify processing capabilities. In a significant development, Tesla recently confirmed the commencement of production at its new lithium refinery in Texas, a facility that broke ground in 2023. This move signals a broader trend, suggesting that if lithium prices continue to climb, we can anticipate increased investment in processing plants outside of China, fostering greater geographical distribution of this critical resource.
Furthermore, 2026 is shaping up to be a pivotal year for the advancement and commercialization of direct lithium extraction (DLE) technologies. As highlighted in recent analyses, DLE utilizes innovative chemical or electrochemical processes to extract lithium from brines, which are essentially salty water sources often found in salt lakes or underground reservoirs. These methods promise to be both rapid and cost-effective, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional evaporation ponds. Major players in the industry, including Lilac Solutions, Standard Lithium, and Rio Tinto, are actively pursuing plans or commencing construction of commercial DLE facilities in strategic locations such as the United States and Argentina. This concerted effort underscores the growing recognition of DLE’s potential to unlock vast, previously inaccessible lithium reserves.
In the dynamic and often unpredictable world of batteries and critical minerals, predicting the future with absolute certainty remains an elusive endeavor. However, if one is seeking indicators of impending shifts and burgeoning trends, the fluctuations in lithium prices offer a compelling narrative. The confluence of surging demand, the ongoing pursuit of technological alternatives, and the strategic recalibration of extraction and processing methods positions 2026 as a watershed year for the lithium market. The decisions made and the innovations deployed in this period will undoubtedly have a lasting impact on the trajectory of clean energy technologies and the global transition towards a more sustainable future. This article is from The Spark, MIT Technology Review’s weekly climate newsletter. To receive it in your inbox every Wednesday, sign up here.