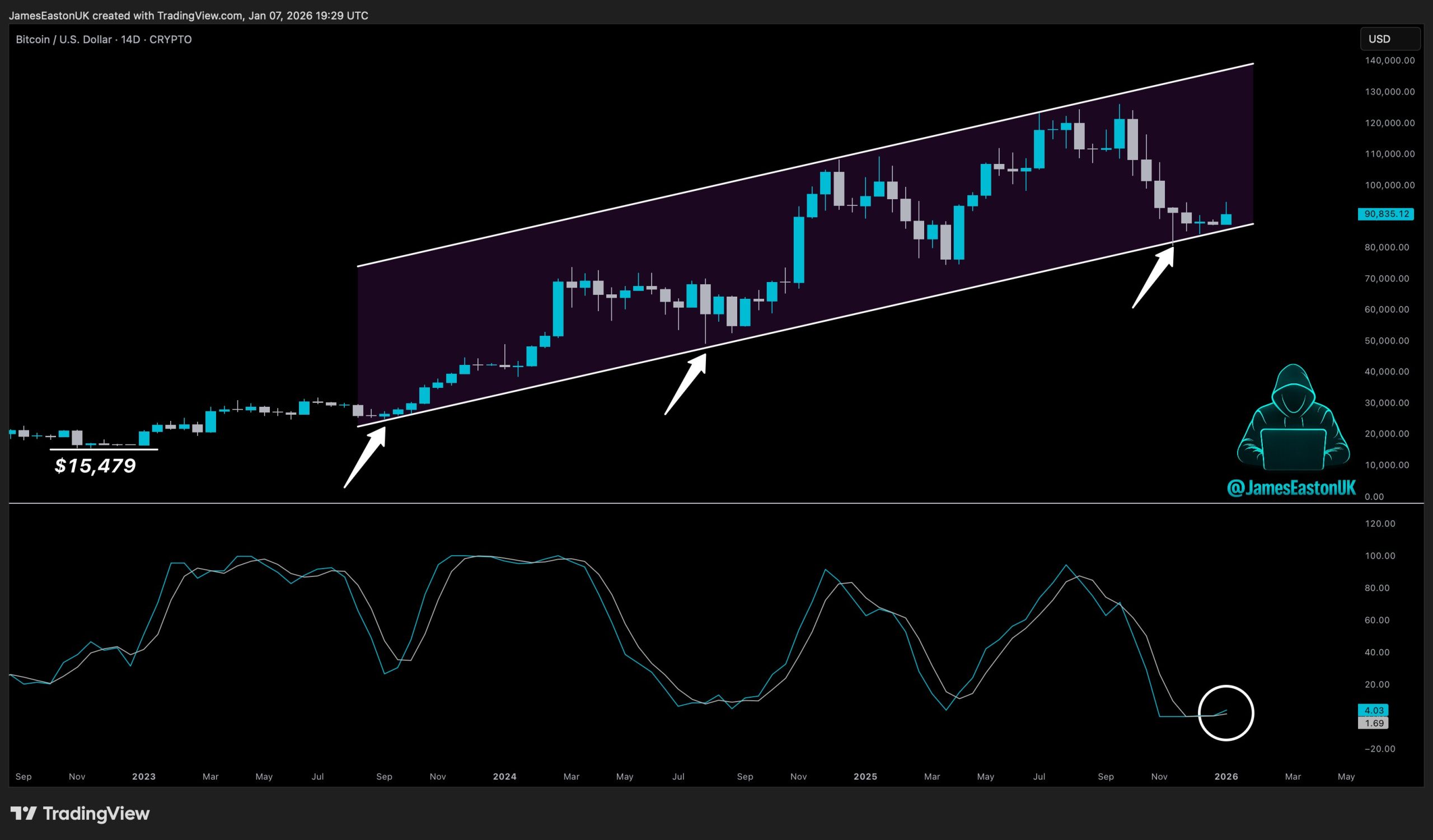
The patent’s emergence arrives at a time when the integration of AI into various aspects of daily life is accelerating, with promises of intelligent agents handling grocery shopping, booking travel, and managing schedules, thereby theoretically freeing up human leisure time. The ironic twist, in Sony’s vision, is that this newfound leisure might then be filled by watching another AI play video games, rather than engaging directly with them. This raises a fundamental question: if an AI plays the game for you, are you still truly gaming, or merely observing an automated performance? Traditionally, the satisfaction derived from video games often stems from the challenge itself – the process of trial and error, the strategic thinking required to overcome obstacles, and the ultimate triumph of personal skill and perseverance. By offering a "Complete Mode" that essentially bypasses this struggle, Sony’s patent could fundamentally alter the psychological reward loop that has defined gaming for decades, potentially diminishing the sense of accomplishment that comes from overcoming a difficult boss or solving a complex puzzle through one’s own efforts.
While the concept of assistance in video games is by no means new, Sony’s AI "Ghost Player" represents a significant technological and philosophical leap. For years, gamers have relied on a spectrum of external and in-game aids, ranging from rudimentary cheat codes and strategy guides to comprehensive online walkthroughs and community forums. Modern titles have also embraced robust accessibility options, allowing players to adjust difficulty levels on the fly, remap controls, or even skip particularly challenging sections to ensure a broader audience can enjoy the narrative or experience. Sony’s own PlayStation 5 console already features a sophisticated Game Help system, which provides easily accessible hints and video guides mid-game, contextualized to the player’s current progress. However, these existing solutions, whether manual or digitally assisted, still require the player to actively process information and execute actions. The "Ghost Player" AI, particularly in its "Complete Mode," shifts the paradigm from assistance to outright automation, effectively removing the human player from the direct decision-making and execution loop.
The proposed "Ghost Player" technology likely relies on advanced machine learning techniques, possibly including reinforcement learning, where an AI agent learns optimal strategies by repeatedly playing the game and receiving rewards for successful actions, or behavioral cloning, where the AI observes and mimics expert human gameplay. Such an AI would need to be incredibly sophisticated, capable of understanding game mechanics, navigating complex environments, making strategic decisions, and adapting to dynamic situations across a vast array of game genres – from fast-paced action games to intricate role-playing games and elaborate puzzle titles. The development and implementation of such a versatile and intelligent system would represent a considerable engineering feat, potentially requiring vast datasets of human gameplay or extensive simulated training environments.
Beyond Sony’s patent, the broader video game industry is already grappling with the pervasive influence of AI. Microsoft, a direct competitor in the console space, introduced its Xbox "AI-driven sidekick" called Copilot for Gaming last year. This feature, built on large language models, aims to coach gamers, offering advice and strategies through voice and text prompts, thereby enhancing their skills rather than replacing them. This distinction is crucial: Copilot for Gaming seeks to empower the player, while Sony’s "Ghost Player" offers to act on their behalf. The use of generative AI in other creative aspects of game development has proven even more controversial. Many gamers and industry professionals have reacted with outright disgust to game studios employing AI for creative tasks such as generating promotional artwork, designing character models, or even synthesizing character voices, raising concerns about artistic integrity, job displacement, and the potential for "soulless" or "slop" content. Despite this backlash, prominent industry figures like Epic Games CEO Tim Sweeney have publicly committed to integrating AI into "nearly all future production," signaling an inevitable and expansive role for the technology within the sector.
The potential benefits of Sony’s "Ghost Player" AI are not entirely without merit. For players with severe physical disabilities, or those facing significant cognitive challenges that prevent them from executing complex game commands, an AI that can play on their behalf could unlock narratives and experiences previously inaccessible. Similarly, time-constrained individuals who wish to experience a game’s story without investing hundreds of hours in mastering challenging gameplay might find value in an AI completing tedious or difficult sections. It could also serve as an advanced tutorial system, demonstrating optimal strategies in real-time, or as a "story mode" for games where the narrative is paramount but the gameplay mechanics are overly punitive. However, these benefits must be weighed against the potential downsides. The "Ghost Player" could foster a generation of passive consumers who lose the intrinsic motivation to develop skills, creating a disconnect between the player and the interactive medium. Critics argue that the essence of gaming lies in active participation and problem-solving, and outsourcing these core activities to an AI risks devaluing the very art form.
The debate surrounding AI in gaming is multifaceted and deeply emotional for many players. As journalist Mike Drucker predicted for The Gamer, 2026 could be "the year that AI in gaming gets super annoying," reflecting a growing sentiment of frustration and skepticism among the gaming community regarding how developers and studios intend to leverage this rapidly advancing technology. The concern isn’t just about job security for artists or writers; it extends to the integrity of the gameplay experience itself. If AI begins to play games for players, it blurs the lines between interactive entertainment and a glorified cinematic experience, potentially eroding the unique appeal of video games as a medium that demands active engagement.
Ultimately, whether companies will fully embrace AI agents that play video games on behalf of players remains to be seen, but Sony’s patent unmistakably signals that such possibilities are actively being explored at the highest levels of the industry. The existence of the "Ghost Player" patent serves as a compelling indicator of the direction technological innovation is heading, challenging traditional notions of gameplay and interaction. It forces a critical examination of the balance between accessibility and challenge, convenience and accomplishment, and the evolving relationship between human players and their increasingly intelligent digital companions. The future of interactive entertainment may well involve AI playing an ever-larger role, but the extent to which players will accept or reject an AI that assumes control of their virtual destinies will be a defining factor in shaping the next era of gaming.