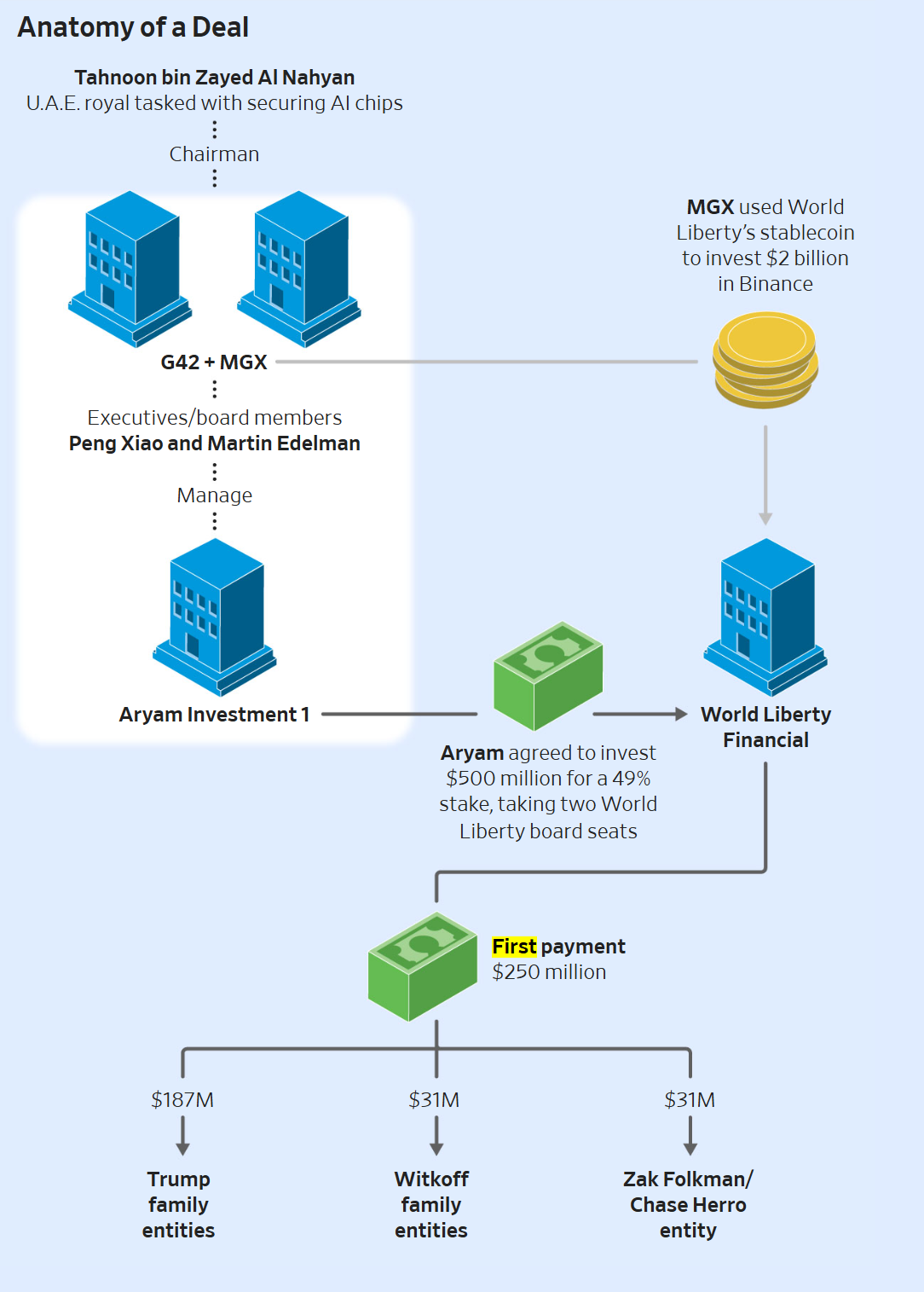
The surge in funding was not evenly distributed; rather, it was significantly bolstered by a series of supersized funding rounds that injected massive capital into a select group of high-growth, AI-focused companies. These mega-deals skewed the overall investment figures, highlighting a trend where investors are concentrating larger sums in fewer, more promising ventures. According to Crunchbase data, at least seven cybersecurity companies successfully closed funding rounds of $400 million or more in 2025. Leading this pack was Cyera, an AI-powered data security platform, which alone secured an astounding $940 million across two separate rounds. Cyera’s success exemplifies the market’s appetite for solutions that leverage AI to protect the rapidly expanding digital footprint of organizations, particularly in data-intensive environments where traditional security measures often fall short. Their platform likely addresses the complex challenges of data sprawl, compliance, and real-time threat detection, making it indispensable for enterprises grappling with sophisticated cyber threats.
Another standout performer was Saviynt, a provider of an identity security platform that caters to both human users and AI agents. Saviynt’s ability to secure a remarkable $700 million round, led by KKR, with a valuation estimated around $3 billion, underscores the growing recognition of identity as the new perimeter in cybersecurity. As organizations adopt more AI-driven processes and manage diverse digital identities, robust identity governance and administration (IGA) solutions become paramount. Saviynt’s focus on integrating identity security with the needs of the AI era positions it at the forefront of this critical domain. Furthermore, NinjaOne, an endpoint management automation and security provider, also made significant waves, securing $500 million in Series C funding early in the year. Their investment signifies the ongoing importance of endpoint protection and management in a hybrid work world, where endpoints are often the first line of defense against cyberattacks. The combined impact of these and other significant rounds demonstrates a strong belief in the foundational and innovative security technologies these companies offer. For a broader perspective, the year’s largest cybersecurity-related funding rounds showcased a vibrant ecosystem ripe with innovation and substantial financial backing.
Despite the impressive rise in total investment, 2025 also presented a nuanced picture regarding deal activity. Paradoxically, while capital inflow soared, the overall number of deals actually declined. The market saw just under 1,000 reported cybersecurity financings last year, marking the lowest total in at least a decade. This trend suggests a "flight to quality" among investors, where capital is increasingly concentrated around a smaller number of high-potential, often later-stage, startups rather than being spread across a wider array of early-stage ventures. This consolidation reflects a maturing market where proven business models, strong leadership teams, and compelling technological differentiation are key to attracting significant funding. While the 2025 tally for deal counts is expected to see a slight uptick over time due to the inherent delays in reporting some seed rounds to public datasets, the underlying trend of fewer, larger deals remains evident. This shift implies a higher bar for startups seeking initial funding and a more competitive environment for those aiming to scale.
However, amidst the overall contraction in deal volume, early-stage investment carved out a significant success story. The early-stage segment, encompassing Series A and Series B rounds, posted a remarkable gain in 2025, with more than 300 reported deals. This figure surpassed the deal count observed in each of the two preceding years, signaling a healthy pipeline of innovative new companies. The financial commitment to early-stage ventures was particularly robust, with $7.5 billion invested in these rounds, representing a whopping 63% increase from year-earlier levels. This pronounced growth was largely fueled by heightened investor enthusiasm for companies operating at the intersection of artificial intelligence and security. Early-stage investors are actively seeking out the next generation of cybersecurity solutions that leverage AI for predictive threat intelligence, automated defense, and enhanced operational efficiency. This focus on AI-driven innovation at the nascent stages of company development suggests a forward-looking investment strategy, anticipating the future needs of the cybersecurity market.
Geographically, the United States maintained its dominant position in the cybersecurity investment landscape. A significant 74% of all funding directed to the space in 2025 flowed into U.S.-headquartered startups, according to Crunchbase data. This continued leadership by American companies can be attributed to several factors, including a robust venture capital ecosystem, a vast domestic market for security products, a deep talent pool in technology and cybersecurity, and a culture of innovation. U.S.-based companies not only attracted the lion’s share of funding but also generated the largest and most impactful exits, further solidifying the country’s status as a global cybersecurity hub. While other regions are certainly developing their own vibrant security sectors, the scale and maturity of the U.S. market continue to draw significant investor interest and drive major industry developments.
The robust funding environment was further validated by a series of high-profile exit events, encompassing both significant mergers and acquisitions (M&A) and successful initial public offerings (IPOs). These exits provided liquidity for investors and founders, while also reshuffling the competitive landscape and highlighting the immense value of cutting-edge cybersecurity technologies. The headline deal of the year, though yet to be finalized, was Google’s planned acquisition of cloud security giant Wiz for an astounding $32 billion. This potential mega-deal underscores the strategic importance of cloud-native security platforms and the premium placed on solutions that can secure complex multi-cloud environments. Wiz’s rapid ascent and Google’s willingness to commit such a vast sum illustrate the critical role advanced cloud security plays in the digital transformation journeys of enterprises.
Another significant acquisition materialized in late December when ServiceNow announced an agreement to acquire Armis, a provider of cyber risk management tools, for $7.75 billion in cash. This acquisition strategically expands ServiceNow’s capabilities, allowing it to offer more comprehensive cyber exposure and security solutions across the full attack surface, including IT, operational technology (OT), and medical devices. The convergence of IT and OT security, driven by the increasing digitalization of industrial and healthcare systems, makes Armis’s expertise particularly valuable. On the IPO front, the standout event for 2025 was the September debut of network security provider Netskope. The Silicon Valley-based company, recently valued around $6 billion, went public, offering investors an opportunity to participate in the growth of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) solutions. Netskope’s IPO signals strong market confidence in the SASE model, which integrates networking and security functions into a unified, cloud-native service, essential for securing distributed workforces and cloud applications. These major exits collectively paint a picture of a dynamic market where innovation is rewarded, and strategic consolidation is actively shaping the future of cybersecurity.
For a sector that thrives on identifying and mitigating risks, cybersecurity seemed to navigate the investment environment of 2025 with remarkably little to fret about. The prevailing sentiment was overwhelmingly positive. Companies that demonstrated a compelling ability to integrate artificial intelligence into their solutions found investors eager to write substantial checks. The confluence of escalating cyber threats, increasing regulatory pressures, and the universal need for robust digital protection has made cybersecurity an indispensable expenditure for businesses of all sizes. Moreover, the receptive exit markets, characterized by significant M&A activities and successful IPOs, provided clear pathways for liquidity and validation, further encouraging investment. While the cybersecurity industry, by its very nature, must always be vigilant for unforeseen risks—there always are—the current outlook remains exceptionally strong. The continuous evolution of AI, the ongoing digital transformation across industries, and the persistent ingenuity of threat actors ensure that the demand for sophisticated security solutions will only continue to grow, promising a sustained period of innovation and investment in the years to come.
The data presented in this report is derived directly from Crunchbase, based on reported figures as of January 4, 2026. It is important to note that data lags can occur, particularly at the earliest stages of venture activity, meaning seed funding amounts often increase retrospectively after the close of a quarter or year. All funding values are presented in U.S. dollars unless explicitly stated otherwise. Crunchbase meticulously converts foreign currencies to U.S. dollars using the prevailing spot rate on the date the financial events, such as funding rounds, acquisitions, and IPOs, are officially reported, even if added to the database at a later date. The consistent application of this methodology ensures accuracy in financial reporting. The glossary of funding terms defines seed and angel rounds as encompassing seed, pre-seed, and angel investments, along with venture rounds of unknown series, equity crowdfunding, and convertible notes up to $3 million. Early-stage funding includes Series A and Series B rounds, along with other round types, for investments between $3 million and $15 million. Late-stage funding covers Series C, D, E, and subsequent lettered venture rounds, as well as corporate venture and other rounds exceeding $15 million. Technology growth refers to private-equity rounds raised by companies that have previously secured a venture round, indicating a more mature growth stage. This rigorous methodology underpins the comprehensive insights into the cybersecurity investment landscape of 2025.