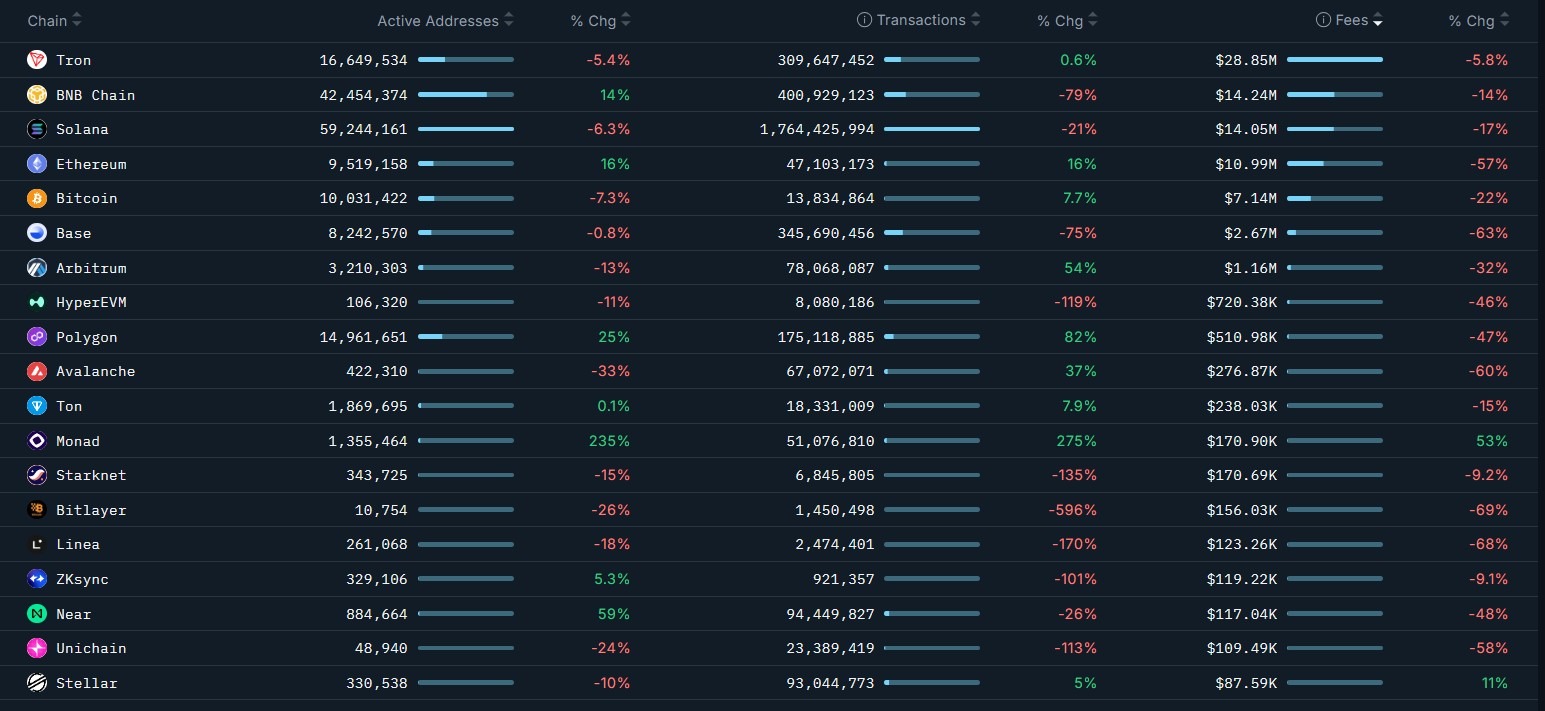
Nansen’s detailed analysis, accessible via their macro blockchain dashboard, highlighted an impressive month-over-month increase in transactions across a diverse array of prominent networks, including Bitcoin, Tron, Ethereum, Arbitrum, Polygon, Avalanche, and The Open Network (TON). Crucially, this growth in activity was paralleled by a sharp decline in fee revenue during the same period, indicating a healthy expansion of network capacity without triggering the dreaded bidding wars for block space that have historically plagued busy chains. This trend is a testament to the ongoing innovation in blockchain architecture, from Layer 2 solutions and rollups to fundamental protocol enhancements.
Ethereum, the behemoth of decentralized applications, witnessed a robust 16% increase in transactions, a remarkable feat considering the concurrent 57% drop in fee revenue. This dramatic decoupling of activity and cost is a direct result of strategic protocol upgrades. Similarly, Polygon, a leading Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, exhibited an even more pronounced divergence: transaction counts soared by an astonishing 82%, while fees simultaneously receded by 47%. Arbitrum and Avalanche also mirrored this encouraging pattern, demonstrating significant transaction growth alongside notable reductions in fees, reinforcing the broader narrative of easing block space pressure across a multitude of networks.
Even networks with more established transaction profiles, such as Tron, Bitcoin, and TON, contributed to this overarching trend. Tron recorded a modest yet consistent 0.6% growth in transactions, Bitcoin saw a 7.7% increase, and TON experienced a 7.9% uptick. Crucially, all three chains also registered declines in fee revenue, further solidifying the evidence that the industry is moving towards an era of higher throughput and lower costs. This widespread phenomenon suggests that the collective efforts to enhance blockchain infrastructure are yielding systemic benefits, making decentralized applications and services more economically viable for a wider user base.
These trends collectively point towards a profound structural shift in how blockchains manage and respond to demand. The continuous rollout of scaling upgrades, the maturation of rollup technologies, and the introduction of more cost-effective execution environments have collectively expanded network capacity to an unprecedented degree. This expansion has enabled a surge in transactional activity without triggering the traditional symptoms of congestion, such as network slowdowns or escalating transaction fees driven by fierce competition for inclusion in blocks. It represents a significant step forward in resolving the blockchain trilemma—the challenge of simultaneously achieving decentralization, security, and scalability—demonstrating that innovative architectural designs can deliver on the promise of scalable decentralized systems.

It is important to contextualize Nansen’s percentage-change figures, as their methodology reflects shifts relative to recent activity baselines rather than strict month-over-month comparisons. As explained in Nansen’s artificial intelligence help section, this approach means that sharp reversals or significant outflows can sometimes register as declines greater than 100%. Such figures denote a net negative flow in activity momentum, rather than literal "negative transactions," providing a nuanced view of dynamic network behavior.
The remarkable increase in transactions coupled with a decline in fee pressure across major networks can be attributed to specific, impactful upgrades implemented recently. Ethereum, for instance, significantly enhanced its capacity on November 27 by raising its block gas limit to 60 million. This critical adjustment, allowing a greater number of transactions and complex contract calls to be processed within each block, immediately began to alleviate network congestion. The benefits of this change were further amplified in December with the deployment of the "Fusaka upgrade." A key component of Fusaka was the introduction of PeerDAS (Proto-Danksharding), a groundbreaking advancement designed to dramatically expand data availability. By making data more readily and cheaply accessible for Layer 2 rollups, PeerDAS effectively reduced aggregate fee pressure across the entire Ethereum ecosystem, even as overall activity surged. This move is a crucial step towards Ethereum’s long-term vision of Danksharding, aiming for massive scalability and ultra-low transaction costs.
Polygon followed a similar trajectory of improvement after deploying its "Madhugiri hard fork" in early December. As Cointelegraph previously reported, this strategic upgrade was engineered to slash consensus time to a mere one second, boosting transaction throughput by up to 33%, and making gas-intensive operations more efficient and predictable. Polygon strategically positioned these enhancements to cater to burgeoning sectors like stablecoin payments and real-world asset (RWA) tokenization. These use cases inherently generate a high volume of frequent, but typically low-urgency, transactions. The Madhugiri hard fork’s ability to handle this increased volume without spiking fees makes Polygon an increasingly attractive platform for enterprise and financial applications seeking predictable and cost-effective blockchain interactions. This aligns with Polygon’s broader vision, including Polygon 2.0, which aims to create an "Internet of Blockchains" with seamless interoperability and scalability.
Avalanche’s impressive performance, characterized by rising transactions and falling fees, appears to stem from a synergistic blend of diverse ecosystem activities. Insights from Nansen Research’s Avalanche Ecosystem Report for Q3 2025 indicated that the network’s robust transaction growth is largely attributable to the increasing adoption of stablecoin payments, institutional settlement solutions, and a burgeoning array of consumer-facing platforms, particularly in ticketing and gaming. These specific use cases are inherently high-throughput but typically do not generate intense competition for block space, allowing transaction volumes to swell without exerting upward pressure on fees. Avalanche’s unique architecture, with its C-chain, X-chain, and P-chain, allows for specialized functionalities that contribute to its overall efficiency and scalability, making it well-suited for these varied applications.
Meanwhile, Arbitrum’s consistent pattern of transaction growth coupled with fee moderation eloquently reflects the inherent economics of rollup scaling. As a leading Layer 2 solution for Ethereum, Arbitrum efficiently batches numerous transactions off-chain and then posts a highly compressed summary of this data to the main Ethereum blockchain. This ingenious mechanism allows transaction volumes to expand dramatically without incurring proportional increases in fees on the expensive Layer 1. Furthermore, Arbitrum’s sophisticated fee market design cleverly separates execution costs from the more substantial Ethereum calldata costs. This separation dampens fee volatility, ensuring a more predictable and user-friendly experience even under considerably higher network loads. This approach embodies the power of optimistic rollups in extending Ethereum’s capabilities and making it more accessible.

While the prevailing narrative was one of expanding capacity and falling fees, not all networks experienced this positive divergence. A segment of the blockchain landscape saw both activity and fee revenue decline in tandem, reflecting a quieter on-chain environment over the last 30 days for these specific chains. BNB Chain, for instance, experienced a sharp pullback, with transactions plummeting by 79% and fees declining by 14%. This suggests a significant reduction in network utilization or a shift of activity to other platforms during the period.
Similarly, Base and HyperEVM recorded some of the steepest contractions in activity. Base transactions fell by 75%, accompanied by a 63% drop in fee revenue. HyperEVM followed a comparable pattern, with transactions down by an alarming 119% (indicating a substantial negative shift relative to its baseline, as per Nansen’s methodology) and fees falling by 46%. These synchronized declines strongly suggest reduced short-term usage across these networks throughout December.
Even Solana, which consistently maintains its position as one of the busiest networks, handling an impressive 1.7 billion transactions in the period, experienced a contraction. This result marked a 21% month-on-month decrease, according to Nansen, with its fee revenue also dropping by 17%. While still a powerhouse of transaction volume, this decline could be attributed to a natural cooling after periods of intense memecoin activity or other specific ecosystem events that drive transient surges in usage.
These synchronized declines across certain networks generally align with broader crypto market conditions observed during the period. According to CoinGecko, the overall crypto market capitalization fluctuated within a relatively narrow range of $2.9 trillion and $3.1 trillion throughout December. With prices, volatility, and capital rotation remaining largely stagnant, it is plausible that on-chain activity across some networks naturally cooled in parallel, reflecting a more cautious or less speculative market sentiment. The provided image illustrating Solana transactions over the last 180 days would likely show a peak followed by this recent dip, visually reinforcing the trend.
In conclusion, the Nansen data unequivocally highlights a transformative period for the blockchain industry. The ability of major networks to process significantly more transactions at substantially lower costs is a monumental achievement, signaling that years of research and development in scaling solutions are now yielding tangible results. This era of enhanced efficiency and reduced friction is poised to unlock new possibilities for decentralized applications, making Web3 technologies more accessible, affordable, and practical for mainstream adoption. As the industry continues to innovate, with further advancements in sharding, modular blockchains, and sophisticated rollup architectures on the horizon, the foundation is being laid for a truly scalable and globally impactful decentralized future. The journey towards mass adoption is being accelerated by these technical triumphs, promising a more inclusive and robust digital economy.