The decision, which took effect on Monday, December 29, 2025, marks a significant shift in the operational landscape for Binance users in Ukraine, particularly those accustomed to the convenience of converting their digital assets into fiat currency via widely used card networks. According to a notice disseminated to affected customers and subsequently reported by several prominent Ukrainian news outlets, including Minfin.com.ua, the suspension specifically impacts direct withdrawals to bank cards issued by both Visa and Mastercard. While the announcement may initially appear abrupt to some users, a Binance spokesperson confirmed the changes to Cointelegraph, clarifying that the "announcement regarding changes to payment methods applies exclusively to users from Ukraine who previously used Bifinity services." This distinction is critical, as it points to the underlying cause of the service interruption: the cessation of operations by Bifinity UAB, Binance’s fiat payment provider.
Bifinity UAB had previously been instrumental in facilitating a range of fiat on-ramp and off-ramp services for Binance users, connecting the crypto exchange to traditional financial rails. The catalyst for Bifinity’s departure from the market stems from evolving regulatory mandates. As early as December 15, Binance had proactively informed its user base that Bifinity UAB would cease offering its services by the close of the month due to unspecified "regulatory changes." At the time of that initial communication, Binance sought to reassure its community, stating that while some fiat on- and off-ramp payment methods would be affected, users’ fundamental ability to deposit, withdraw, buy, or sell crypto would continue "without interruption." The current suspension of card withdrawals, however, represents a partial deviation from this initial assurance, at least concerning the immediate ease of converting crypto to fiat via card networks. This highlights the complex and often fluid nature of navigating the global regulatory landscape for cryptocurrency exchanges, particularly when dealing with third-party payment processors who themselves are subject to stringent financial regulations.
The implications for Ukrainian users extend beyond just direct card withdrawals. Local reports further indicate that Binance has also notified its customers that recurring crypto purchases and any existing fiat-based limit buy orders will not be processed during the period of suspension. This means users who had set up automated investment strategies or specific price-point buy orders using fiat currency might find their plans temporarily disrupted. The cumulative effect of these changes could lead to a degree of inconvenience for users relying on these specific functionalities for their crypto management and investment strategies.
However, it is crucial to note that the core functionality of fiat on-ramps largely remains intact for Ukrainian users, underscoring Binance’s efforts to maintain accessibility where possible. Users can still deposit funds and purchase cryptocurrencies using their Visa and Mastercard for incoming transactions. Furthermore, modern digital payment solutions such as Apple Pay and Google Pay continue to be available options for topping up accounts, providing alternative avenues for users to bring funds into the Binance ecosystem. For both deposits and withdrawals, SWIFT transfers, a long-standing method for international money transfers, remain fully supported. This offers a viable, albeit potentially slower and more traditional, route for users to move significant sums of fiat currency in and out of the exchange. The Binance spokesperson emphasized that these changes are "not related to the National Bank of Ukraine" and crucially "do not affect P2P operations, which continue to function as usual." This latter point is particularly significant in regions where traditional banking channels might be challenging or less accessible, as peer-to-peer trading often serves as a resilient alternative for crypto liquidity.

Adding another layer of complexity, the update also impacts the availability of Zen.com, a payment platform frequently utilized for transactions involving Euro (EUR) and Polish Zloty (PLN). Binance has indicated a temporary disruption to Zen.com’s full deposit and withdrawal functionality for its Ukrainian users. The exchange has, however, provided an anticipated resumption date for these services, with full functionality expected to be restored on January 6, 2026. Until then, users who typically rely on Zen.com for their EUR and PLN transactions will need to explore alternative methods, such as the aforementioned SWIFT transfers or the robust peer-to-peer trading options available on the platform, where legally permitted. This patchwork of available and temporarily unavailable services reflects the dynamic environment in which cryptocurrency exchanges operate, constantly adapting to regulatory shifts and the capabilities of their financial partners.
This localized service adjustment in Ukraine comes at a time when Binance is once again facing intensified scrutiny on a global scale. A recent investigative report by the Financial Times cast a shadow over the exchange’s compliance efforts, alleging that Binance permitted a cohort of potentially suspicious accounts to continue facilitating crypto fund movements, even after committing to stricter controls as part of its monumental $4.3 billion US criminal settlement in 2023. The report detailed that these 13 linked accounts collectively processed an estimated $1.7 billion in transactions since 2021, with a staggering $144 million of that activity occurring after Binance entered its plea agreement with the U.S. Department of Justice in November 2023. These transactions reportedly involved users across several jurisdictions deemed high-risk, raising questions about the effectiveness of Binance’s enhanced anti-money laundering (AML) and sanctions compliance frameworks post-settlement.
The 2023 settlement was a landmark event for Binance, resolving charges that included operating an unlicensed money-transmitting business, money laundering, and sanctions violations. As part of this agreement, Binance’s founder and former CEO, Changpeng Zhao (CZ), stepped down and pleaded guilty to failing to maintain an effective AML program. Richard Teng was appointed as the new CEO, tasked with steering the exchange towards a new era of stringent regulatory compliance. The settlement also mandated the appointment of an independent compliance monitor, whose role is to oversee Binance’s adherence to the terms of the agreement for several years. The Financial Times report, therefore, directly challenges the perceived progress of Binance’s compliance overhaul, suggesting potential lapses or challenges in fully implementing the required controls.
In response to the Financial Times allegations, Binance vehemently rejected the report’s framing. The exchange communicated to Cointelegraph that all transactions in question were rigorously assessed based on the information available at the precise time of their occurrence. Furthermore, Binance asserted that none of the wallets involved in the transactions mentioned in the report were subject to sanctions at the point when the activity took place. This defense highlights a common challenge in financial compliance: the real-time nature of sanctions lists and the difficulty of retroactively applying new information or designations to past transactions. However, the ongoing nature of such reports, coupled with the significant fines and compliance obligations, underscores the intense pressure on Binance to demonstrate robust and proactive adherence to global financial regulations.
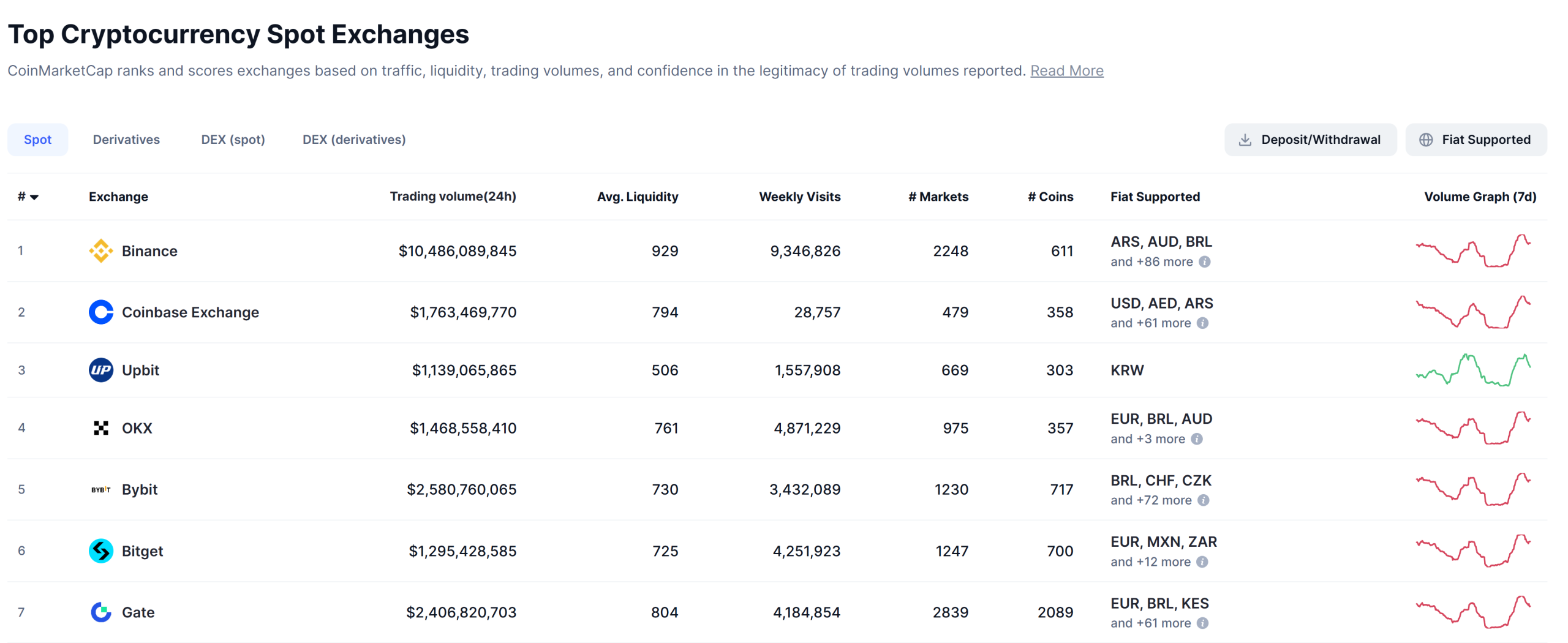
The situation in Ukraine, while distinct in its immediate cause (Bifinity’s withdrawal due to regulatory changes), is nonetheless intertwined with the broader narrative of Binance’s ongoing efforts to navigate an increasingly complex and demanding regulatory environment worldwide. The temporary suspension of specific services, even if framed as a consequence of third-party actions, adds to the operational challenges faced by the world’s largest crypto exchange by volume, a position it maintains as evidenced by platforms like CoinMarketCap. These incidents collectively shape public perception, influence user trust, and can potentially impact the strategic decisions of an exchange striving to rebuild its reputation and ensure long-term sustainability in a heavily scrutinized industry. For Ukrainian users, the immediate imperative is to adapt to the revised payment landscape, utilizing the remaining fiat channels or leaning more heavily on the resilient peer-to-peer trading ecosystem to manage their digital assets effectively. The dynamic nature of the crypto industry, particularly in regions affected by geopolitical instability, continues to demand agility and adaptability from both platforms and their users.