The annual gathering of the world’s elite in Davos, Switzerland, often serves as a crucible for emerging global trends, and 2026 proved no exception for the digital asset space. Amidst discussions on climate change, AI ethics, and international security, the discourse around crypto moved beyond mere technological curiosity to become a full-blown debate on economic power, regulatory frameworks, and geopolitical competition. At the forefront of this collision was a stark contrast in perspectives: the United States, under President Donald Trump, championed crypto as a strategic national asset, while major European central banks expressed profound skepticism, warning against the destabilizing potential of private digital money.
US President Donald Trump dedicated a significant portion of his much-anticipated Davos speech to reiterating his administration’s ambitious goal: to cement the United States’ position as the undisputed global capital for cryptocurrency innovation and adoption. His rhetoric underscored a clear pivot from earlier, more cautious stances on digital assets, signaling a robust commitment to fostering a crypto-friendly legislative environment. Trump’s vision, as articulated, was not merely about economic growth but was deeply intertwined with national security and technological dominance. He emphasized that embracing crypto was a crucial component of maintaining American leadership in the rapidly evolving digital economy, perceiving it as a new frontier for innovation, job creation, and attracting global talent. This forward-leaning stance aimed to provide regulatory clarity and foster an ecosystem where blockchain technologies could flourish, attracting investment and entrepreneurial spirit that might otherwise migrate to more permissive jurisdictions.
This pro-crypto messaging from the White House stood in stark contrast to the cautious, often critical, tone emanating from traditional financial institutions, particularly central banks. In a highly anticipated panel discussion featuring prominent crypto industry leaders, Françoise Villeroy de Galhau, the Governor of the Bank of France, delivered a pointed critique of private money, specifically targeting yield-bearing stablecoins. His concerns centered on the potential for such private digital currencies to undermine financial stability, erode monetary sovereignty, and complicate central banks’ ability to conduct effective monetary policy. De Galhau passionately advocated for the proliferation of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), positioning them as the sovereign, stable, and regulated alternative that could modernize financial infrastructure without relinquishing democratic control over money. He argued that money, as a public good, must remain firmly within the purview of state authority, echoing a sentiment widely shared among his central banking peers across Europe and beyond.
The chasm between these two philosophies highlighted that while crypto had undeniably arrived on the Davos stage, a global consensus on its role and regulation remained elusive. The US political narrative framed crypto adoption and robust regulation as a necessary geopolitical maneuver, a competitive weapon in the race for technological supremacy and economic influence. Conversely, the European central banking perspective viewed private crypto, particularly stablecoins with their potential for global reach and interest-bearing features, as a direct threat to national financial stability, monetary policy efficacy, and the very concept of sovereign money. This fundamental disagreement became the most visible point of contention, setting the stage for ongoing debates and divergent policy paths in the years to come.
Here are the specific crypto takeaways from Davos 2026 that further illuminate this fascinating collision of politics and money:

Trump Frames Crypto Regulation as a Geopolitical Race
President Donald Trump, in a special address on Wednesday, made a declarative statement regarding the future of crypto legislation in the United States, expressing his fervent hope to sign a comprehensive crypto market structure bill "very soon." This bill, widely recognized as the CLARITY Act, had been a subject of intense lobbying and debate, slated for a crucial US Senate markup the previous week. However, its progress was unexpectedly stalled after major crypto industry players, notably Coinbase, reportedly withdrew their support. This setback underscored the complexities and internal disagreements within the crypto industry itself, even amidst a generally favorable political winds.
Trump’s framing of US crypto regulation was not merely about economic efficiency or innovation; it was imbued with a sense of geopolitical urgency and national security. "It is politically popular but much more importantly, we have to make it so that China doesn’t have a hold of it, and once they get that hold, we won’t be able to get it back. So I’m honored to have done it," Trump declared, linking the current legislative push to his earlier signing of the GENIUS Act, a foundational piece of legislation for stablecoins. His comments revealed a strategic calculus: preventing China, or any rival nation, from establishing dominance in the digital asset space, particularly in foundational technologies like blockchain and digital currencies, was paramount to safeguarding American financial and technological sovereignty. The administration viewed a robust and well-regulated domestic crypto industry as a bulwark against foreign influence and a critical component of maintaining a competitive edge in the global digital economy. The White House’s ambition to transform the US into the world’s leading crypto capital was thus presented as a competitive imperative, with regulation serving as a strategic tool to foster innovation while mitigating risks. Despite the CLARITY Act’s current legislative limbo, Trump spoke with an air of inevitability, suggesting its passage was a matter of when, not if, reflecting his administration’s unwavering commitment to this strategic objective.
The gravitas of Trump’s address was further amplified by his introduction by Larry Fink, the CEO of BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager. Fink’s presence, representing the traditional financial behemoth that has increasingly embraced crypto, symbolized the growing convergence of mainstream finance and digital assets. While Trump’s speech spanned over an hour, covering a wide array of domestic and international policy, the dedicated segment on cryptocurrency, though brief, resonated profoundly, signaling its elevated status on the global political agenda.
Coinbase CEO and French Central Banker Clash Over Money Sovereignty
One of the most defining and widely circulated crypto moments at Davos occurred during a panel discussion where the philosophical divide between decentralized finance advocates and traditional monetary authorities was laid bare. Françoise Villeroy de Galhau, the Governor of the Banque de France, delivered a nuanced but ultimately critical assessment of private cryptocurrencies, even as he acknowledged the transformative potential of tokenization. De Galhau stated that "tokenization and stablecoins are likely to be the name of the game" in 2026, recognizing their capacity to significantly modernize financial infrastructure, particularly within wholesale markets. He lauded Europe’s ongoing central bank digital currency (CBDC) efforts, presenting them as a global benchmark for responsible digital monetary innovation. This praise for tokenization, however, quickly faded as the discussion veered towards the contentious issue of monetary sovereignty.

Brian Armstrong, CEO of Coinbase, offered a contrasting vision, positioning Bitcoin (BTC) as a "modern successor to the gold standard." He argued that Bitcoin’s decentralized, immutable nature serves as a crucial check on unchecked governmental deficit spending and inflationary policies, offering an independent, apolitical store of value. Armstrong articulated a libertarian ideal, where a global, permissionless digital currency could provide an alternative to traditional fiat systems, empowering individuals and fostering greater economic freedom.
Villeroy de Galhau swiftly pushed back against this narrative, asserting that money is inextricably linked to sovereignty and state authority. He argued that ceding control over monetary systems to private entities would effectively amount to a surrender of a fundamental function of democracy and national governance. This perspective underscored the central banker’s deep-seated concern that private digital currencies could undermine a nation’s ability to manage its economy, control inflation, and implement fiscal policies, thereby eroding its sovereign power.
Armstrong countered by highlighting Bitcoin’s decentralized structure, claiming it offered an even greater degree of independence than traditional fiat systems, which are ultimately subject to political whims. He characterized the tension between public and private money as a "healthy competition," a remark that elicited a wry chuckle from Villeroy de Galhau, signifying the irreconcilable differences in their foundational beliefs.
The French central banker further drew a firm line against interest-bearing stablecoins, expressing concerns that their yield-generating mechanisms could destabilize the existing financial system by siphoning deposits from traditional banks and creating new avenues for systemic risk. US crypto executives on the panel, however, argued that offering rewards or yields was a necessary competitive measure, crucial for attracting and retaining users, especially in a global landscape where rival digital currencies, such as China’s CBDC, might offer their own incentives. This exchange vividly illustrated the ongoing struggle to define the boundaries of financial innovation and regulatory oversight in the digital age.
Binance Leaves Door Open to US Return
The question of Binance’s future in the highly coveted US market garnered significant attention at Davos. Richard Teng, Binance’s co-CEO, adopted a cautious yet optimistic "wait-and-see" approach in an interview with CNBC on the sidelines of the forum, declining to make definitive commitments but deliberately leaving the door open for a potential return. This measured stance reflected the complex regulatory and legal challenges Binance has faced in the US.

The company had launched Binance.US in 2019 as a distinct entity to comply with US regulations, yet faced severe repercussions when US regulators alleged that the parent company continued to service "VIP" customers through its offshore platform. This culminated in a landmark 2023 Department of Justice settlement, where founder Changpeng Zhao (CZ) pleaded guilty to failing to maintain an effective Anti-Money Laundering program, leading to a jail sentence. In a surprising turn of events that underscored the shifting political landscape, Zhao was later pardoned by President Trump.
Ripple CEO Brad Garlinghouse, in a separate interview, was far more explicit in his predictions, confidently asserting that Binance would eventually make a full return to the "very large" and strategically important US market. Garlinghouse’s conviction likely stemmed from the sheer scale and economic power of the US crypto market, which remains an irresistible draw for global players.
Zhao himself, fresh from his pardon, was notably present at Davos and actively participated in a panel discussion on Thursday. His presence alone was a powerful symbol of his continued influence and the enduring resilience of the crypto industry. During the panel, Zhao confidently declared that crypto had unequivocally proven its staying power, asserting that it was "not going away."
Interestingly, despite their different panels and perspectives, Zhao found common ground with the Bank of France’s Villeroy de Galhau on the transformative potential of tokenization. Zhao hailed tokenization as the "next phase of the industry," alongside artificial intelligence and payments, recognizing its capacity to unlock immense value. He revealed that he was actively engaged in discussions with "about a dozen governments" regarding the tokenization of state-owned assets, envisioning this as a powerful mechanism to unlock latent value, stimulate economic development, and provide new avenues for investment and liquidity. This convergence on tokenization highlighted a shared vision for modernizing finance, even if the underlying philosophies on monetary control remained divergent.
Circle’s Allaire Calls Bank Run Fears Absurd
The debate around stablecoins continued with Jeremy Allaire, CEO of Circle, stepping in to robustly dismiss fears that interest-paying stablecoins could pose a systemic risk to the traditional banking system. In a Thursday panel discussion in Davos, Allaire branded such concerns as "totally absurd."

Allaire argued that the incentives involved in stablecoin yields are simply "too small to threaten monetary policy or drain deposits" on a scale that could destabilize the broader financial landscape. He emphasized that these interest payments primarily function as a customer retention tool, designed to make stablecoins more attractive and competitive for users, rather than acting as a systemic disruptor capable of triggering widespread bank runs.
To support his argument, Allaire drew a compelling historical comparison to government money market funds. He pointed out that despite repeated warnings and prophecies of doom over the years, approximately $11 trillion has flowed into money market funds without ever collapsing bank lending or triggering systemic crises. This historical precedent, he suggested, demonstrated that the financial system has mechanisms to absorb and adapt to shifts in capital allocation without catastrophic consequences.
Furthermore, Allaire highlighted a broader, ongoing trend: the gradual shift of lending away from traditional banks towards private credit and capital markets. He contended that this fundamental re-architecture of financial intermediation is occurring independently of stablecoins, suggesting that the concerns being raised were either misplaced or exaggerated in the context of broader market evolutions. His argument aimed to de-escalate the perceived threat of stablecoins, repositioning them as a natural evolution within a dynamic financial landscape rather than an existential danger.
What Davos Revealed About Crypto Priorities
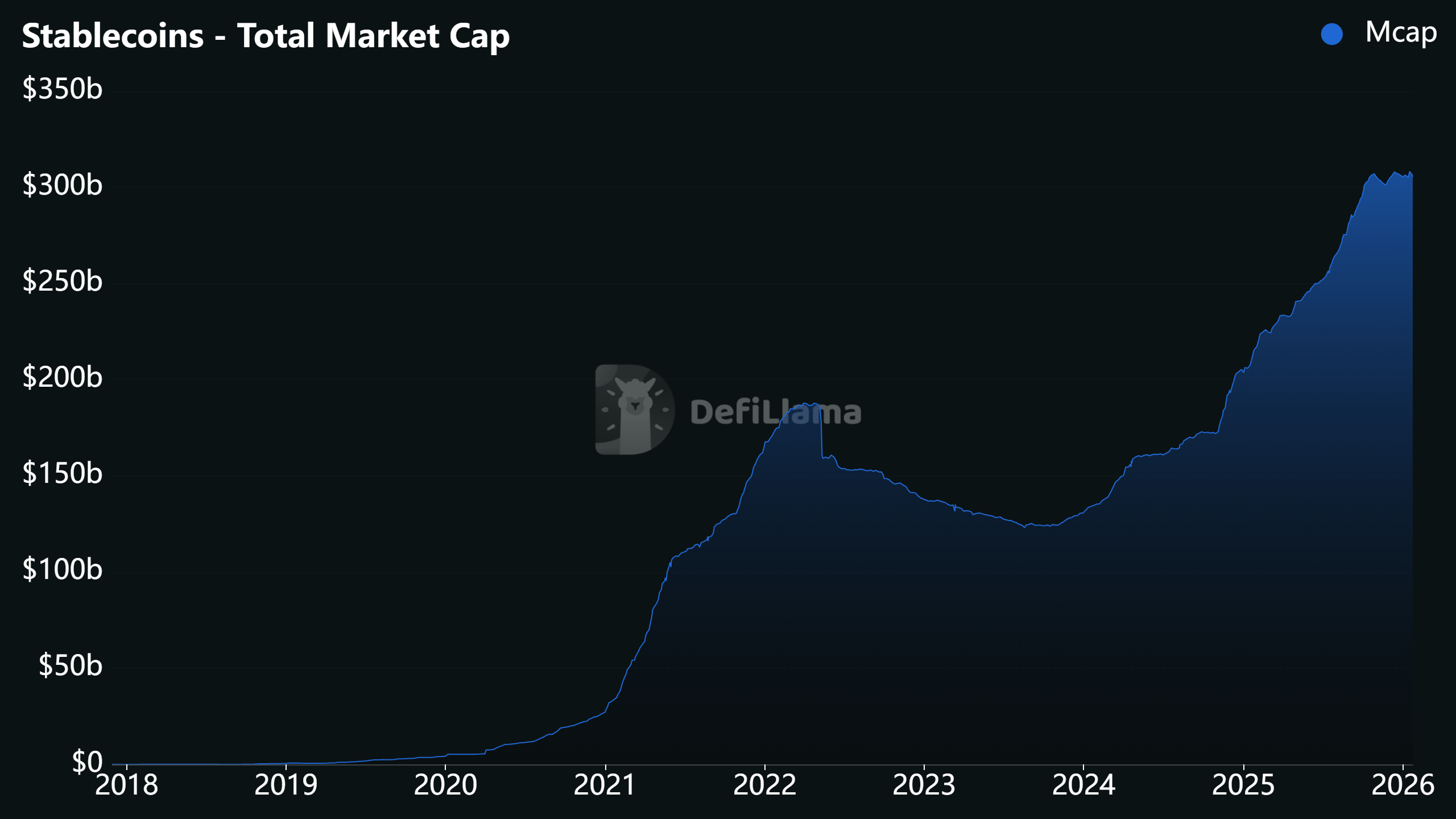
Davos 2026 underscored a remarkable evolution in the narrative surrounding stablecoins. Just a few years prior, in 2022, the public image of stablecoins had been severely tarnished by the spectacular multibillion-dollar collapse of the Terra ecosystem, which began with its algorithmic stablecoin, TerraUSD (UST), backed by the native LUNA token. This catastrophic failure triggered a "crypto winter" and fueled intense regulatory scrutiny, leading many to question the viability and safety of the entire stablecoin concept.
However, by 2026, the narrative had demonstrably flipped. Stablecoins, far from being dismissed as a fringe or dangerous innovation, had ascended to become a core topic of discussion at the annual meeting of the world’s most influential voices in geopolitics and economy. Even central bankers, traditionally the most vocal critics of the broader crypto industry, now acknowledge stablecoins, alongside tokenization, as central themes deserving serious attention and policy consideration. This shift reflects a maturing industry, improved stablecoin designs, and a growing recognition of their utility in cross-border payments, digital finance, and potentially as a bridge between traditional and decentralized finance.

Davos 2026 therefore reinforced that stablecoins and tokenization are not merely fleeting technological trends but integral components of the ongoing global policy conversation. The gathering highlighted that while the US executive branch and Europe’s banking sector remain philosophically divided on the optimal approach to regulating and integrating these digital assets, the debate is no longer about if they will be integrated, but how. Regulatory developments, however, continue to be constrained and shaped by domestic politics, national interests, and the ongoing ideological struggle between centralized control and decentralized innovation. The future of global finance, as unveiled at Davos 2026, will be a complex interplay of these competing visions, forging a new era where politics and money collide in the digital realm.